-
Startup India
- Startup India Standup India
- What is Startup India portal
- Overview of the Indian Startup Ecosystem
- Here are some problems india facing (Ideas for New Startup)
- Expand Business in India
-
Registration
- Business Registration
- Introduction
- Company Registration
- Proprietorship Registration
- Partnership Registration
- Limited Liability Partnership
- One Person Company Registration
- Private Limited Company Registration
- Public Limited Company Registration
- Special Entity Registration
- Section-8 Company Registration
- Trust Registration
- Society Registration
- Industry Specific Registration
- Fssai Registration
- Import Export Code Registration
- Tax Registration
- GST Registration
- PF ESI Registration
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Trademark Registration
- Copyright
- Certification
- ISO Certification
- Things to do After Incorporation
- Stage-1 : Basic Necessity
- Stage-2: Industry Specific Necessity
- Stage-3: Go Live & Get Funding
-
Compliance
- Startup Compliances
- Introduction
- Company Law Compliances
- ROC Annual Compliances
- ROC Event Compliances
- Tax Compliances
- GST Compliances
- Income Tax Filing
- BookKeeping & Accounting
- PF ESI Compliances
-
Go Online
- Development of Aura of Your Business
- Website Development
- Mobile Application Development
- CRM Development
- Content Writing
- Blog Writing
- Video Production
- Plugins and APIs
- Retargeting & Remarketing
-
Tutorials
- Startup Related Tutorials
- Tax Benefit for Startups
- Get Fund from Angel Investors
- Get Fund from Venture Capitalists
- How to Startup Recognize
- Start India Eco-system
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojna
- Credit Guarantee for MSME
- GeM Portal
- What Govt doing For Startups
- Thing Keep in Minds Before Startup
- One Reason Behind Startup Failure
- How to Increase Team Productivity
- Aatmanirbhar Bharat
- Women Entrepreneurship Platform
- Legal Drafting
- PSB loans in 59 minutes
- 10 Strategy for Startup Success
- Business Registration Tutorials
- Proprietorship Registration
- Partnership Registration
- Limited Liabilty Partnership
- OPC Registration
- Private Limited Company Registration
- Public Limited Company Registration
- Nidhi Company Registration
- Section-8 Company Registration
- Non-Profit Organization
- Trademark Registration
- ESI/PF Registration
- FSSAI Registration
- Import Export Code Registration
- ISO Certification
- Naming Guidelines
- Type of Business Registration
- NITI AAYOG Registration
- Compliance Tutorials
- Change Company Registered Address
- ROC Annual Compliances
- GST Registration & Compliances
- Startup Compliances
- LLP Compliances
- Income Tax in India
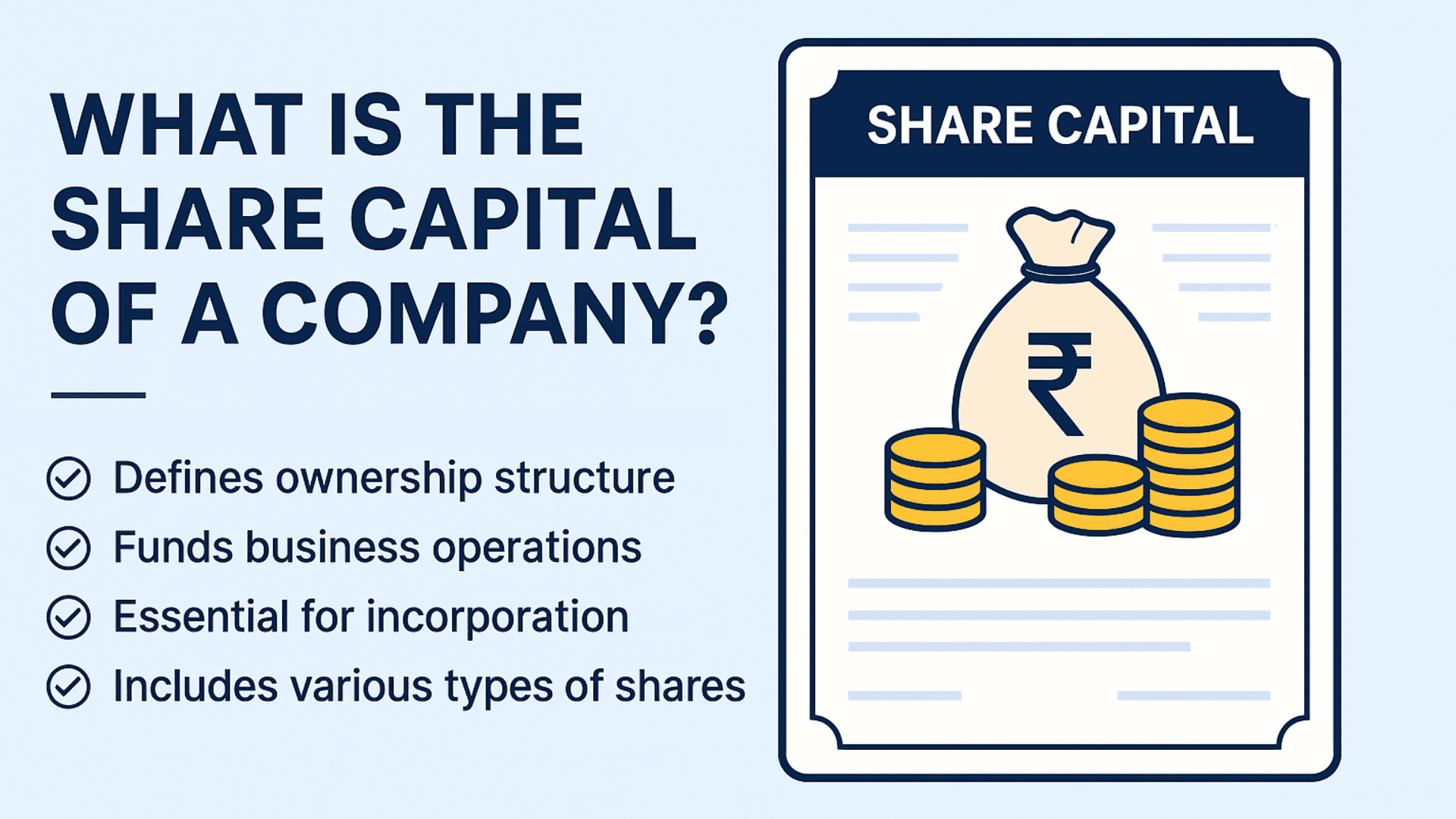
- Share Capital
- How to Change Company Name
- Change in Company Objective
- Cost of Non Compliances
- Is Business Accounting is important
- TDS and ITS Returns
- Benefits of filing ITR
- Tax Audit
- Income Tax Return Filing
- Notices Issued Under the Income Tax
- Income Tax Slabs
- Digital Marketing Tutorials
- How to Develop CRM
- How to Generate Leads
- How to Write Blog
- How to Develop Mobile App
- How to Develop Website
- How to Create Videos
- Online Business
- How to Create Content
- Ecommerce Website
- Landing Pages
- Video Marketing
- Facebook for Business
- Startup Marketing Strategies
- Build Online Presence
- Adwords
- Lead Generation
- Digital Marketing
- Downloads
- Packages
- Login/Sign Up
India’s 1st Startup Consulting Company Earns YouTube Silver Button